1. Introduction
he term digital marketing and e-tourism can be described as the process of production and communicating the tourist experiences via the media, telecommunication, information, show biz technologies in the tourism destinations (Benckendorff, et al, 2014). The digitalization of tourist experience in the tourism industry is often referred to as E-tourism. (Buhalis, 2011). The logical application of digital media activity has transformed the management of art and science in the tourism industry (Buhalis & Law, 2008), because in the last decade e-tourism marketing have witness tremendous influence in the marketing of all e-tourism products. (Whitelaw, 2008).
Recent findings have confirmed that the essential feature in the production and consumption of online tourism experience is derived from the digital technology. Hence, most remote tourism destinations have now shown increased interest in technology related resources, knowledge and capabilities (Benckendorff, Sheldon & Fesenmaire,2014;Werthner et al., 2015). Therefore, tourism in Africa is one of the top export sectors in the emerging countries and its ranks third after petroleum, chemicals and automobile supplies as documented by (UNWTO, 2017). Previous research recognized that the world's foremost tourist arrivals are mostly in Africa which represent the main growth area for leisure and tourism with high economic advancement due to its position as the source of foreign exchanged earnings in export diversification for Africa. (UNWTO, 2017).
The African Travel and Tourism Association (Atta) and World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) in their contribution to the growth of International tourist's arrival in Africa revealed astonishing results with 62.7 million increase in tourist's arrival in 2017. Likewise, UNWTO, (2018, 2019) reported an upsurge of 67 million growths in 2018. So therefore, it can be deduced that Africa has recorded worth $36.2 billion upturn in the global tourism receipts in 2016 (African Development Bank, 2018). Additionally, statistical findings also revealed that about $194.2 billion was realized in African Tourism which indicated the growth of nearly 8.5 percent as the gross domestic product (GDP) in 2018 (Atta, 2019;WTTC,2018). Accordingly, 10.2 million was realized as tourist's influx from South Africa in 2017. While 11.3 billion was recorded by Morocco and 28,000 was recorded by Comoros as revealed by (UNWTO, 2018; Azeez, 2019).
WTTC, (2019) also revealed some of the African countries that recorded a high GDP growth in the World Travel and Tourism, these countries include: Ethiopia which recorded (+48.6 percent) in 2018. It has been established that Egypt has recorded approximately +16.5 percent of international tourist's growth. Consequently, the aggregate numbers of tourist influx has created huge opportunities for Africa and managing strategic marketing technological advancement has accounts for 45% market share indicating that tourism arrivals are significantly higher than the 31% market shared realized in 1990.Based on this progress, the UNWTO predicted that tourism destinations in Africa will grow in astonishing rate far more than those of the developed nations (UNWTO, 2018, 2019).
According to Yasmin et al (2015) the promotion of e-tourism in relation to marketing of products and services is supported by computerized media. Digital tourism marketing in Africa has been recognized as an information channel for the internet users and Facebook platforms usage; (Internet World Stats, 2019). Findings in relations to digital marketing statistics reveals that South Africa has recorded 28.6 million representing 52 percent used the internet, while 15 million users were using the social media platforms which represents approximately 70 percent on a weekly basis on social media platforms. Consequently, findings also revealed how crucial the social media marketing promote digital tourism products (Digital Statistics in South Africa, 2017).
Hence, digital marketing technology performance a vital role in sustaining the competitive advantage of new digital field in promoting tourism product online. The integration of mobile phones, internet websites and augmented reality experience in the marketing of e-tourism products are becoming a global positioning systems among the forms of digital marketing technologies cutting-edge as a dominant digital element for suppliers, tourism intermediaries, tourists and online destination promoters (Benckendorff, Sheldon, & Fesenmaier, 2014). This is also true with local tourism marketers whose interest is to work together and increase awareness in the promotion of online tourism marketing technique (Morrison, 2013) ). Thus, literature on etourism and digital marketing has continued to be associated to the concept of Small Medium Enterprise (SME). For example, Pradhan, Oh & Lee, (2018) conducted a study in India which revealed the need for African countries to examine the prospects that can be derived from digital tourism marketing. This research was designed following the outcome of Pradhan et al. (2018). Similarly, Yamen also advised that e-tourism marketers should acknowledged the efficiency of digital marketing in the challenging age Yasmine et al, (2015). This research explores e-tourism and digital marketing with particular focus to opportunities and challenges in Africa. The study will enhance the body of literature in etourism and online marketing by improving the marketing competencies of destination marketing organizations and e-tourism managers in Africa by provide relevant information updated in e-tourism products, since many tourism organizations promote their products and services via digital marketing.
2. a) Area of Study
This study examined e-tourism and digital marketing in Africa: opportunities and challenges by focusing on the statistical growth of international tourist's arrival as compiled by the United Nation World Tourism organizations (UNWTO), stating from 2015 -2019. However, the study is limited to only five African regions which include Northern Africa, Eastern Africa, Western Africa, Central Africa and Southern Africa AS depicted in Figure 1. The study is limited to only five top selected African regions as mentioned earlier for the purpose of this research.
Source: Facts and maps (2018) Figure 1 II.
3. Literature Review a) Conceptual Clarifications
i. E-tourism E-tourism has been defined as a 'travel technology' or "e-travel" in tourism activities. In other words, e-tourism denotes a phenomenon in the study area that embraced the information and communication technology (ICT) by business travelers, tourists and other value chains in the tourism sector. This progress has no doubt altered the process within which organizations reconfigure the landscape of marketing (Buhalis 2003).
4. ii. Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is referred as the marketing of tourism products and services via the electronic media with the sole aim of capturing customers to interact with the tourism product through digital media (Yasmin et al., 2015). One of the most significant method in Social media marketing is the application of online marketing (Chaffey, 2011). The marketing of tourism product online through via online websites, opt-in, interactive Television, interactive Kiosks, mobile phone or online advertisement (Chaffey and Smith, 2008).
Mandal, Joshi & Sheela, (2016) described digital marketing as a brand advertising through the application of available types of publicity through the media t-in order to stimulate prospective marketing segment. This study explores e-tourism and digital marketing in Africa: opportunities and challenges, which essentially means the promotion of online tourism products and services via digital publicity media like the Facebook, often referred to as the social media.
b) The Competitive Advantage theory (Porter, 1990) The theory of competitive advantage was employed in order to gained strategies of developing or acquiring a set of qualities that can furnish tourism organization with the appropriate strategy to outperform its competitors. The theory of competitive advantage was formed by Porter, (1990) and he presumed that a nation can be successful if it shaped by organizations that has achieved profitable marketing expertise throughout the world market, which is rest on the ability to transform and improvement their market talents (Porter, 1990;Gupta, 2015).
Past studies have revealed the important opportunities that can be derived from as a +-9advantage through the application of new technological strategies (Porter & Millar, 1985). *-Yasmin, Tasneem, & Fatem, (2015) specified that digital marketing signifies the numerous advertising techniques designed to reach consumers through the internet for marketing tourism product. The internet platform can generate a good strategic means of boosting trade and competitive advantage (Mandal, Joshi, & Sheela, 2016).
For easy comprehension the researchers tried to explained in a tabular representation previous scholar that employed the competitive advantage theory in table I to support their claims as a crucial element of etourism and digital media marketing in Africa (Elly & Boter, 2014;Dirsehan, 2015;Jani & Minde, 2016). The study summarized the findings of various researchers by identifying some vital key areas such as: authors involved in the research, type of study employed, country where research is conducted and the outcomes of the study. Bang and Roos (2014) in their own contribution surveyed digital marketing concentrating on digital marketing approach paying attention on industrialized industries by applying the qualitative methodology and established that small-and medium-sized businesses regularly apply online digital marketing through the homepage sites. This research lay emphasis on etourism and marketing using digital means to evaluating the influx of tourists. Table I: presents the influx of tourist's growth in Africa starting from 2000, 2014, 2017 and 2018 respectively.
Thus, Bala and Verm, (2018) carried out critical evaluation of e-tourism and digital marketing in Africa to determine the present and future trend in marketing etourism products specifically in the India environment. The findings of this study shows strong reform regarding digital marketing which gives customers who are searching for internet information about tourism activities. However, successful online marketing is guided by key factors that gives customers assurances to utilizing social media sites as advised by tourism organizations (Bala and Verm, 2018). Further, some researchers identified that the nature of tourism marketing via social media was time-consuming for most owners including emotional benefits of social media which include social, and economic reason (Canovi and Pucciarelli, 2019).
Information about the diffusion of internet penetration rate in terms of population percentage in in Africa as of June 30, 2019 Within the Nigerian population about 50 percent of the population are using smartphone. This is a great opportunity for Nigeria to explore consumers using mobile marketing known as smartphones. Past research findings has demonstrated the significance of mobile technology and its role in allowing consumers relates with their service providers such as hotels through the websites using different kinds of device (Murphy et al., 2016; Smith, 2017; Ukpabi and Karjaluoto, 2017).
Stringam & Gerdes (2019) highlighted the significance of improved load times in capturing prospective customers who contact hotel websites so that they can access time easier and faster. In addition, about 80 percent of Africans used mobile phones as revealed by internet statistics (The Global Digital Report, 2019). Tables I, II and III demonstrate the internet statistics in terms of population and penetration rate. Hence, subscription was also selected and used as a platform for product awareness and the communication with consumer, upgrade response tool. Equally, Begho (2019) revealed five (5) African products in 2019 by forecasting the product through online digital marketing which include: integrated marketing through strong communications, user experience, creative content, customer capital and block chain technology. Empowering Effect: One of the prospects of digital marketing is related to special influence in enabling small businesses flourish on the internet as it extents rapidliy to reach large group of audience as well as efficiently reach small and medium enterprises (SMEs) (Dholekia & Kshetri, 2004). In fact, online marketing create a kind of democratized environment in which Problem of Integrity: Digital marketing has been an essential theme of the profession (Clow & Baak, 2013). One of the challenges with digital marketing promotion is that they use several numbers of offline and online advertising networks such as brochures, newspapers, press media as marketing frameworks. Each item is used in isolation and accomplished as a
5. Global Journal of Management and Business Research
Volume XXI Issue I Version I Year 2021 ( ) marketing has been restructured in such a way that even small businesses are given a good chance to promote their products on a more larger scale (Tapp, 2008) different task not as an element of a combined marketing campaigned designed at creating awareness of definite purpose (Bostanshirin, 2014) 2
Eliminates Geographical Impediments: Using digital marketing has the advantage of reaching unlimited global audience in practices of buying and selling, thereby eliminating the burdens that geographical locations could impact in marketing medium reach (Sigala, 2008).
Lack of Face-to-Face Contact: One of the key problem in e-tourism and digital marketing is the deficiency of lack of personal. These difficulties have been criticized specifically in digital marketing competencies (Goldsmith & Goldsmith, 2002). Most consumers prefer face-to-face marketing which is known as personal interaction, this is because consumers believe that they can talk to store personnel selling the product (one-on-one) through personal contact and this will give them the opportunity to touch and feel the product with hands. Hence, this will build customer relationship management (CRM) between the buyer and seller (Kiang &Chi, 2001). they can touch and feel the products with their hand, because this act will build a personal relationship between the buyer and the seller (Kiang & Chi, 2001).
6. 3.
Available 24 hours\7 days: Digital marketing furnished the consumer with timely information because it operates 24 hours in a day, and 7 days a week (Lane, 1996). There is no time limitation in opening or closing time in digital marketing business, thereby overpowering the geographical obstacles. Therefore, tourism and hospitality marketers can distributes products for different market segment of the market with no conditions (Mohammed, 2010).
Security & Privacy: In today's involving world digital marketing needs information to be shares with utmost privacy in the electronic world. It is very clear nowadays that customers top personal details are share with other companies without asking for their opinion or permission. In addition, other vital personal data such as users name and passwords are easily high jacked by internet scammers (Lantos, 2011).
7. Cost-Effective:
IT can be deduced that compared with traditional marketing, which is the old-style way of advertising media channels, digital marketing is very resourceful. Distribution of products and services via internet is evidently cost-effective and can accomplished its objectives at a very little cost (Poon & Jevons, 2010).
8. Lack of Trust:
Trust is defined as an online consumer perception of how a website would delivers expectation, believable information's and how confidents the websites commands its image (Bart et al, 2005) the problem of insecurity is mostly derived from the absence of trust. Customers need trust to help them eradicate challenges in the parts of customers which has been acknowledged as a huge challenge in digital marketing growth. This why digital marketing expectation in relation to trust is increasingly growing in importance in tourism and hospitality study (Urban, et al, 2009). Source: Authors III.
9. Method
This exploratory research is limited specifically to Africa as a case study. Content analysis was employed to reviewed literature in this research. The reviewed literature approach employed what is characterized as integrative literature review procedure. Review literature has been recognized as research method by which the past and current scholars used in qualitative research (Torraco, 2005(Torraco, , 2016;;Snyder, 2019). The integrative literature reviewed articles applied in this research includes reports, online publications, conference papers, and journals that acknowledge etourism and digital marketing with reference to opportunities and challenges in Africa.
According to Torraco (2005) integrative literature is defined as a desktop study that analyzed criticisms and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in a much-integrated manner given way to new framework and viewpoints on the topic are produced. In addition, Torraco (2016) refer to integrative literature assessment as a unique form of research that applies existing literature in new knowledge creation. Equally, Snyder (2019) emphasized in the promotion of literature review as a new kind of research method in tourism and business studies
Other prominent researchers such as Babori et al., (2019) joined thematic content analysis and literature review approach to carryout research specifically on the role and place of content for massive open online educations. Consequently, this research used the integrative literature review approach and the content analysis to review literature in relation to e-tourism and digital marketing in Africa with the aim of exploring etourism and digital marketing with particular reference to opportunities and challenges in Africa, by paying specific attention on testing social media marketing examining international tourist's influx in five (5) African regions as mentioned earlier.
IV.
10. Discussions
The literature reviewed and content analysis in table I signifies that the use of competitive Advantage Theory in Digital marketing has been recognized by past and current tourism scholars. Likewise, Table II A consideration in addressing these challenges reveals that there will be biggest improvement opportunities for digital marketing in Africa to create a positive international tourist flow and digital metrics.
V.
11. Conclusion
Conclusively, this study focused on exploring digital marketing and e-tourism in Africa as a case study. Social media marketing has amazing opportunities in terms of marketing using mobile and content marketing. Recent findings about mobile marketing in Nigeria reveals that about 50% of the population has registered substantial number of smartphone users as well as Facebook subscribers in the social media marketing. These interprets clearly that digital marketing requires, innovative\content marketing and mobile promotion to developed online promotional trends marketing trends that can boost and increase of international tourist influxes in Africa tourism.
12. VI.
Implications for Tourism and Hospitality Industry
Implication for knowledge and practice revealed that, for digital marketing strategy to progress, stakeholders in the tourism industry must think digital act digital by using social media marketing through the innovation of novel skills in using content and mobile promotion as the new technology in focus for marketing tourism in Africa.
The theoretical implication of this study has demonstrated that Nigeria as a country will have remarkable competitive advantage compared to other African countries. Nigeria has registered strong presence and leading capacity in promoting tourism growth by the using the digital media to market tourism and hospitality product. The application of mobile promotion and text messages will inspire the sharing of tourism contents by most internet to enhance the digital marketing of domestic and international tourists influx in Africa.
Similarly, Egypt has shown great competitive advantage skills with high number of Facebook subscribers over other African countries using social media marketing. Egypt has recorded A tremendous opportunity specifically in utilizing high rate of digital marketing through the application of social media marketing to increase the development of tourism. Additionally, African statistical records in e-tourism and digital marketing have also presented that the second largest country in terms of internet user is Ethiopia. However, the country is not listed among the best top five (5) internet users in Africa.
This study suggests that countries like Ethiopia should be encouraged to embrace the light of social media marketing by using the internet in cutting-edge for the advancement of tourism industry in their country. Further Tanzania came fifth in the lists of African with high population and ranks third as the highest internet user. This implies that, compares to other African countries like South Africa, Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania has by clear miles' act as a leading country with great potentials and competitive advantage in population and internet users.
13. VII.
14. Limitations of the Study
This study is limited to literature review and content analysis technique as a research method. Future studies should employ both qualitative and quantitative methods to have deeper understanding of the digital marketing phenomenon in managing and advancing tourism trades.
| tourism industries for tourism managers who need to | |||
| understand information that relates to statistical influx of | |||
| tourists. | |||
| c) Theoretical Underpinning | |||
| i. E-tourism and Digital marketing | |||
| Previous research findings about e-tourism and | |||
| digital marketing has been investigated by Chaffey, | |||
| (2011) Waghmare (2012), Gangeshwer (2013), Kumar | |||
| and Jincy (2017) Yasmin et al. (2015), and Lies (2019). | |||
| Yasmin et al. (2015) also carried out a research | |||
| to understand the | |||
| Year 2021 | |||
| Volume XXI Issue I Version I | |||
| ( ) | |||
| Authors (Year) Adeleye, (2015) Examined the social Types of Study media marketing challenges Jani & Minde (2016). They explored the theory of competitive advantage in tourism destination in East Africa Odyssey (2019) Investigated the opportunities of Digital statistics | Research Country Africa Tanzania & Uganda, Nigeria | Outcome of the Study\Findings He projected that marketing intelligence can be utilized by marketers as a passive marketing advert to serve as a promotion means for brand awareness. Findings revealed the competitive advantage for Uganda was visitors service and accommodation and visitor services While transport system and Travel motivation was identified as advantage for Tanzania. Found that Nigeria has been identifies having 17 million social media active users and tag among the best trending digital marketing medium in 2019. This signifies that there are many business potential marketing opportunities to explore. | Global Journal of Management and Business Research |
| Hence, there are high population of smart phones | |||
| users in Nigeria | |||
| African | 2000 | 2014 | 2017 | 2018 |
| International tourist arrivals | 26million | 56million | 62.7million | 67million |
| African Countries by | Population | Internet Users in | Internet Users in June | |
| Region | (Million) | December 2000 | 2019 | Subscribers |
| Northern Africa | ||||
| Libya | 6.5 | 10, 000 | 3, 800, 000 | 3, 500, 000 |
| Algeria | 42.6 | 50, 000 | 21, 000 | 19, 000, 000 |
| Tunisia | 11.7 | 100, 000 | 7, 898, 534 | 6, 400, 000 |
| Egypt | 101.1 | 45, 000 | 11, 192, 827 | 35, 000, 000 |
| Morocco | 36.6 | 100, 000 | 22, 625, 872 | 15, 000, 000 |
| Eastern Africa | ||||
| Tanzania | 60.9 | 115, 000 | 43, 662, 499 | 6, 100, 000 |
| Kenya | 52.2 | 200, 000 | 43, 329, 434 | 7, 000, 000 |
| Uganda | 45.7 | 40, 000 | 18, 502, 166 | 2, 600, 000 |
| Burundi | 11.5 | 3, 000 | 617, 116 | 470, 000 |
| Rwanda | 12.7 | 5, 000 | 5, 981, 638 | 490, 000 |
| Ethiopia | 110.1 | 10, 000 | 20, 507, 2554, | 500,000 |
| Source: Compiled from internet World Stats (2019) | ||||
| African Countries by | Population | Internet Users in | Internet Users in June | ||
| Region | (Millions) | December 2000 | 2019 | Subscribers | |
| Western Africa | |||||
| Ghana | 30.1 | 30, 000 | 11, 400, 732 | 4, 900, 000 | |
| Nigeria | 200.9 | 200, 000 | 119, 506, 430 | 17, 000, 000 | |
| Burkina Faso | 20.3 | 10, 000 | 3, 704, 265 | 840, 000 | |
| Cote d'Ivoire | 25.5 | 40, 000 | 11, 192, 827 | 3, 800, 000 | |
| Central Africa | |||||
| Cameroon | 25.3 | 20, 000 | 6, 128, 422 | 2, 700, 000 | |
| Central Africa | 4.8 | 1,500 | 256, 432 | 96, 000 | |
| Republic | |||||
| Chad | 15.8 | 1,000 | 1, 027, 932 | 260, 000 | |
| Congo Dem Republic | 86.7 | 500 | 5, 301, 224 | 2, 100, 000 | |
| Southern Africa | |||||
| Zambia | 18.1 | 20, 000 | 7, 248, 773 | 1, 600, 000 | |
| Angola | 31.7 | 30, 000 | 7, 078, 067 27 | 400, 000 | |
| Zimbabwe | 17.2 | 50, 000 | 8, 400, 000 | 880, 000 | |
| South Africa | 58.1 | 2, 400, 000 | 32, 615, 165 | 16, 000, 000 | |
| Source: Compiled from Internet World Stats (2019) | |||||
| d) Opportunities and Challenges of E-tourism and | services to reach consumers using digital channels. | ||||
| Digital marketing | However, marketers are continuously confronted with | ||||
| Digital marketing is widely used as a means of | new challenges and opportunities specifically in this | ||||
| marketing that promotes e-tourism products and | digital era as shown in Table V as follows: - | ||||
| S\N | Opportunities | Challenges |
| 1 |
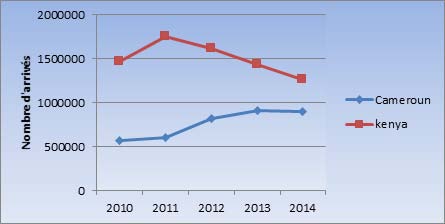
| According to Internet World Statistic, (2019) |
| there are five (5) top countries in African that have |
| been users identified in terms of internet which |
| include: Nigeria which registered 119.5 million, Egypt |
| has (49.2 million), Tanzania with roughly (43.6 million), |
| Kenya having (43.3 million) while South Africa registered |
| (32.6 million) respectively. Similarly, the top 5 African |
| countries in terms of Facebook subscription include: |
| Egypt (35 million), Angola (27.6 million) Algeria |
| (19 million), Nigeria (17million) and, South Africa with |
| (16 million). |
| Furthermore, the top five (5) African countries in |
| terms of population are: Nigeria (200.9 million), |
| Ethiopia (110.1million), Egypt (101.1 milllion) Congo |
| Democratic Republic of Congo (86.7 Million) and |
| Tanzania (60.9 million) internet World statistic, (2019). |
| In addition, findings of the research also |
| identified three (3) potentials challenges in digital |
| marketing by practitioners: |
| o The lack of ability to generate and stimulate deep |
| consumer awareness. |
| o the deficiency in skills to properly manage brand's |
| position in a marketing platform where social media |
| plays important role and |
| o Evaluating the competence of digital marketing. |