1. Introduction
echnology is one of the major influential factors in an Industry. The current era is the age of science and technology and is called as the Fourth Industrial Revolution era. The digital technologies like machine language (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) both are entering into day to day working at the workplace and which will lead transformation in business (Amla & Malhotra, 2017). According to Abrams et al. (2019) in computer science, artificial intelligence is referred as machine intelligence, whereby natural intelligence is less focused now, and machines play the role of intelligence for organizations. Due to increasing pressures in business, artificial intelligence is entering into the overall system of organizations and one of the essential areas is human resource department (Jain, 2017;Yawalker, 2019). The role of artificial intelligence in human resources (HR) helps to support and develop a successful workforce in organization (Abubakar et al., 2019;Buzko et al., 2016) and this motive provides the direction of present study.
2. a) Role of Artificial Intelligence in HR
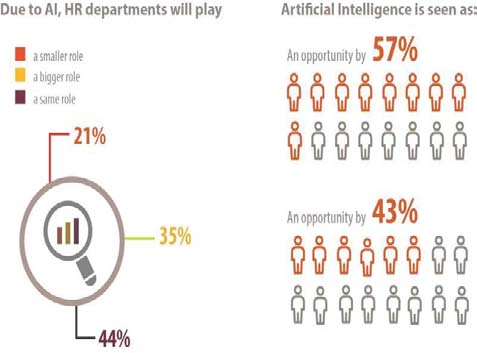
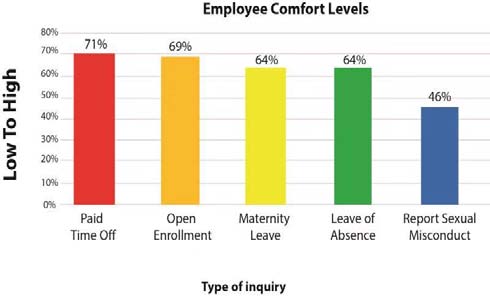
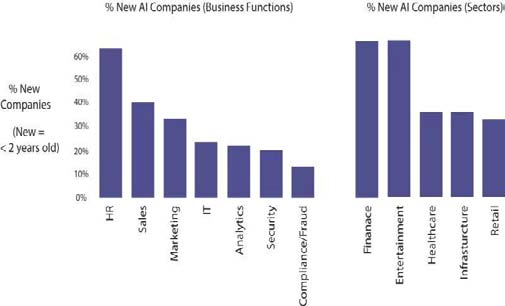
The HR department in organizations is heading towards the digital revolution and using various methods to simplify the resources by using big data analysis, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing (Amla & Malhotra, 2017). Most of the organization has been using artificial intelligence or digital technologies in HR like a chat bot, machine learning, and robot process automation in human resource management, which support recruitment, screening, on boarding, and interviewing etc. The dynamics of artificial intelligence entrepreneurship are increasing with time. Therefore, the application and contribution of AI in various aspects of Human Resource is seen in Figure. II.
3. Literature Review
A heavy strand of literature investigates the role and efficiency of AI in HR management (Buzko et al., 2016;Yu, 2010). Artificial intelligence (AI) is effective in describing machines, systems, and software, efficient in achieving human-like intelligence for problem-solving decisions or individuals' support (De Geofroy & Evans, 2017). Jain (2018) quoted that most of the companies are adopting modern technology in various HR processes like recruitment process, performance appraisal process, cloud-based HR systems. Jarrahi (2018) identifies Artificial intelligence (AI)to be supportive in decision making, dealing with uncertainty, and especially equivocality of decision-making in an organization. ). Additionally, the evolution of the HRIS provides a bas is for AI applications. (Reilly, 2019). HRIS is a process for storing, gathering, retrieving, preserving and authenticating data required by an organization about its HRs, personnel activities, and organization unit characteristics. However, if we have a comparison between AIHRM and information system, the information system deals more with data entry and storing, but still lacks inthe intelligence decision assistance function. (Jia et al., 2018).
AI also directs the attention of organizations towards Knowledge management (KM), which is a strong resource for sustainable competitive advantage in organizations (Abubakar et
4. Methodology
The research intends to investigate the impact of AI on Organizational performance, Employee engagement, and Employee Learning and Development. The study population consists of all nonfinancial organizations listed in Pakistan Stock Exchange (PSX) and the Australian Securities Exchange (ASX). The sample of the study consists of the number of employees and managers working in the selected companies. The data is collected through questionnaire survey research. The collected data is compiled in Statistical Packages for Social Sciences (SPSS) software. The regression analysis is used to observe the impact of AI on organizational human resources in the firms operating in Pakistan and Australia.
5. a) Questionnaire Survey
The respondents of the study consist of IT managers, Unit managers, Supervisor of service desk, Digitalization manager, Incident managers, Contract strategists, Customer managers, IT managers, HR managers, IT architects, Communicators as well as multiple Support personnel. The questionnaire consists of total of 40 questions, 10 questions each related to four variables of the study, named Artificial intelligence, Organizational performance, Employee Engagement, and Employee Training and Development. There was a total of 60 respondents selected, but 48 respondents from each country provided the completed survey while remaining missing questionnaires were excluded from data.
6. b) Regression models
Model-I: ?????? ?? = ?? 0 + ?? IV.
7. Results and Analysis a) Descriptive analysis
The descriptive statistics in Table 2 indicates that the mean values of the data set are between 38 and 40. It indicates that the data set has quite close values. The minimum value of the data set is 20, while the maximum value is 50 for all variables except artificial intelligence in Pakistan. On the other hand, the standard deviation values also indicate that the data of all variables is not dispersed, and there is no indication of an outlier. Hence, the data is normally distributed, and the responses of respondents were almost the same to every question.
8. b) Correlation analysis
The correlation values in Table 3 indicate that all variables of the study are highly positively correlated to each other, and there is no indication of negative or zero correlation. Additionally, in Pakistan, the artificial intelligence is highly correlated to employee training and development in HR while in Australia; the highest correlation is reported between artificial intelligence and organizational performance. Overall, the correlation indicates that artificial intelligence increases HR performance in firms operating in Pakistan.
9. c) Reliability and validity
To check the validity and reliability of the questionnaire, the value of ? is obtained. The value of ? equals 8 indicates that the questionnaire is valid and reliable. The value of ? (0.834) in Table 4 indicates that the questionnaire used for the present study is valid and reliable, and it can be used in further research.
10. d) Regression analysis
The regression analysis of the present study is shown in Table 5, covering both Model-I and Model-II. Model-I presents the relationship of artificial intelligence with HR performance in the case of Pakistan, while Model-II presents the results in the case of Australia. The statistics of the table indicate that both models present the fitness of good, indicating that independent variables used in the present study are sufficient to present effective results. Consequently, the R-square value (0.8339) of Model-I indicates that the independent variables of the study explain 83.39 percent of the data, and these variables are sufficient to generate significant results. Similarly, R-square value (0.8770) of Model-I indicates that the independent variables of the study explain 87.70 percent of the data, and these variables are sufficient to generate significant results. The F-test indicates that the multiple regression models in the present study provide a better fit to the data with the selected variables of the study in both models. Hence, the values of the F-test for Model-I (73.61) and Model-II (104.54) are small, indicating a goodness of fit. Also, the P-value (0.000) of the F-test is significant at 0.01 level or 99% of confidence interval, supporting the results of the F-test.
11. e) Test of multi-collinearity
The presence of the multi-co llinearity in data set is checked through the variance inflation factor (VIF). Table 6 presents the values of VIF. The Mean VIF value indicates the presence of no multi-co llinearity in data.
12. f) Hypotheses testing
According to the regression results of Table 5, the case of Pakistan in Model-I, P-value (0.000) is significant in the case of organizational performance and employee training and development at 0.01 or 99% confidence interval. However, employee engagement does not indicate any significant value. It indicates that artificial intelligence (AI) in Pakistan only increases organizational performance and effective employee training and development. However, HR in enterprises of Pakistan is unable to engage their employees through artificial intelligence yet. Hence, hypotheses H 1 and H 3 are accepted while H 2 is rejected. On the other hand, in the case of Australia in Model-II, the results indicate that P-value (0.000) is significant for all independent variables; organizational performance, employee engagement and employee training and development. Thus, P-value is significant at 0.01 or 99% level of confidence interval. Henceforth, the hypotheses H 4 , H 5 and H 6 are accepted indicating that artificial intelligence (AI) in enterprises in Australia clearly increases their HR performance.
V.
13. Conclusion
An essential part of management in the modern age is computing because rapid changes in the environment of business demands efficient and quick responses. The present study intends to identify the role of artificial intelligence (AR) in empowering the performance of HR in firms operating in Pakistan. However, the performance of Pakistan is compared with Australia in terms of AI application in HR. The results indicate HR in the firms of both countries applies Artificial Intelligence. However, AI is unable to significantly enable employee engagement in the context of Pakistan. Nevertheless, AI successfully increases the organizational performance, and effective employee training and development practices in Pakistan. On the contrary, the application of AI in Australia is efficient in successfully increasing HR performance. Overall, the results reveal that developed countries are more efficient and effective in implementing and adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) compared to developed countries. Further research can be conducted in more than one developed and developing nation, particularly in the application of AI in HR. Moreover, future research can focus on other areas of HR, like talent management, organizational productivity, and employee commitment, etc. Additionally, public enterprises, as well as private enterprises, can be compared in terms of AI application in HR. Eventually, the role of artificial intelligence can be assessed in terms of increased or decreased economic growth overall.
| ; Jarrahi, M. H. (2018) |
| ? H 5 : Artificial intelligence significantly increases |
| employee engagement of firms in Australia. |
| ? H 6 : Artificial intelligence significantly increases |
| employee learning and development of firms in |
| Australia. |
| III. |
| a) Hypotheses: s |
| ? H 1 : Artificial intelligence significantly increases the |
| organizational performance of firms in Pakistan. |
| ? H 2 : Artificial intelligence significantly increases |
| employee engagement of firms in Pakistan. |
| ? H 3 : Artificial intelligence significantly increases |
| employee learning and development of firms in |
| Pakistan. |
| ? H 4 : Artificial intelligence significantly increases the |
| organizational performance of firms in Australia. |
| Where, |
| ?? 0 = Constant or risk or beta factor. |
| ?? 1 , ?? 2 , ?? 3 = Coefficients. |
| ?????? ?? = Artificial intelligence of 'i' firm in Pakistan. |
| ?????? ?? = Organizational performance of 'i' firm in Pakistan. |
| ?????? ?? = Employee engagement of 'i' firm in Pakistan. |
| ???????? ?? = Employee training and development of 'i' firm in Pakistan. |
| ?????? ?? = Artificial intelligence of 'i' firm in Australia. |
| ?????? |
| Variable Obs. Mean | St. Dev. | Min | Max | ||
| P-AI | 48 | 40.85 | 5.93 | 28 | 49 |
| P-OP | 48 | 38.93 | 6.39 | 29 | 50 |
| P-EE | 48 | 39.97 | 6.82 | 20 | 50 |
| P-ETD | 48 | 39.89 | 6.07 | 28 | 50 |
| A-AI | 48 | 39.27 | 6.95 | 23 | 50 |
| A-OP | 48 | 39.08 | 6.48 | 23 | 50 |
| A-EE | 48 | 38.66 | 6.72 | 27 | 50 |
| A-ETD | 48 | 40.22 | 6.14 | 22 | 50 |
| P-AI | P-OP | P-EE | P-ETD | A-AI | A-OP | A-EE | A-ETD | |
| P-AI | 1 | |||||||
| P-OP | 0.843 | 1 | ||||||
| P-EE | 0.829 | 0.731 | 1 | |||||
| P-ETD | 0.873 | 0.786 | 0.897 | 1 | ||||
| A-AI | 0.832 | 0.819 | 0.799 | 0.863 | 1 | |||
| A-OP | 0.833 | 0.768 | 0.942 | 0.914 | 0.898 | 1 | ||
| A-EE | 0.862 | 0.977 | 0.735 | 0.831 | 0.837 | 0.777 | 1 | |
| A-ETD | 0.878 | 0.798 | 0.946 | 0.934 | 0.787 | 0.895 | 0.814 | 1 |
| Variables | Obs. | ? |
| P-AI | 48 | 0.823 |
| P-OP | 48 | 0.849 |
| P-EE | 48 | 0.837 |
| P-ETD | 48 | 0.82 |
| A-AI | 48 | 0.834 |
| A-OP | 48 | 0.827 |
| A-EE | 48 | 0.847 |
| A-ETD | 48 | 0.839 |
| Test Scale | 0.8345 |
| Dependent variable is AI | ||||||
| IV's | Coefficients | Sig. | R-square | F | Prob. F | |
| P-OP | 0.3703 | 0.000*** | 0.8339 | 73.61 | 0.000*** | |
| Model-I | P-EE | 0.1563 | 0.206 | |||
| P-ETD | 0.3895 | 0.013*** | ||||
| A-OP | 0.9288 | 0.000*** | 0.8770 | 104.54 | 0.000*** | |
| Model-II | A-EE | 0.4711 | 0.000*** | |||
| A-ETD | -0.4065 | 0.009*** | ||||
| Note: *** Significant at | ||||||
| 0.01 | ||||||
| Variables | VIF | 1/VIF |
| P-OP | 2.64 | 0.378 |
| P-EE | 5.2 | 0.192 |
| P-ETD | 6.32 | 0.158 |
| A-OP | 5.24 | 0.19 |
| A-EE | 3.07 | 0.325 |
| A-ETD | 6.14 | 0.162 |
| Mean VIF | 4.768 |