1. Introduction
he world economy has changed in the beginning of the 1990s. With the end of the Cold War, the free market economy extent throughout the world leading to a remarkable economic boom. At the same time, social and political clashes have also captured our lives. Also, Wall Street consequences represent the problems of the free market economy. Voracity and irresponsibility often consume those who seek big profits and bonuses. The free market economy cannot end hunger, unemployment, and poverty. In fact, it often causes these problems. The distribution of resources in the world today is unequal and there is a huge gap between the haves and have-nots. The consequences of this imbalanced distribution have caused poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, poor health, and other social problems.
To tackle the social problems and for the purpose of sustainable development, Nobel Laureate and Managing Director of Grameen Bank Prof. Dr. Muhammad Yunus have developed the concept of "Social Business" for the purpose of achieving maximum social benefits. Then, later different scholars explain and introduce this unique concept in different way. Michael Porter has shown some arguments for social enterprise (business) over traditional CSR. Porter wrote: "Corporations must create economic value in a way that also creates value for society by addressing its needs and challenges". Also, Porter lays out his concept of "shared value". Companies are urged to "reconnect company success with social progress" and "take the lead in bringing business and society back together". Porter's arguments and writings are closely associated with Yunus's concept of social business. Prof. Kotlar has written a new book 'Marketing 3.0 (From products to customers to human spirit)'. He has written two entire chapters on social business enterprise as a way to achieve millennium development goals (MDGs), set by the United Nations keeping Prof. Yunus's social business model and Grameen's social business ventures as his focal points. The Guardian-has published an article titled corporate social responsibility (CSR) is dead, long live social enterprise'. What Michael Porter and Philip Kotlar are saying in 2011, the same thing was told by Prof. Muhammad Yunus three years back in 2008 in his book, "Creating a World Without Poverty: Social Business and the Future of Capitalism" and again in 2010 in his another book, "Building Social Business: The New Kind of Capitalism That Serves Humanity's Most Pressing Needs." II.
2. Literature Review
There are a lots of research works on how to start and manage a traditional business. But, a few research is conducted which is not enough for collecting the knowledge about a successful social business.
M. Khalid Shams (2009) describe that Grameen Family of Companies play an important role to solve particularly poverty, and they always work for socioeconomic development of rural people. Now, Grameen family has developed new idea i.e. social business. It is true that they can successfully run the new type of business and building them into financially sustainable ventures within the shortest possible timeframe. Sayema Hoque (2011) explained the basic overview and current trend of social business in Bangladesh and other B countries. Also, show a comparison between social business model and traditional business model. Md. Nazmul Hossain (2011) explicate that the concept of social business should be introduced in our academic curriculum. There are lots of researche works done by the western countries researchers and they already included it as a major course in university level. This idea is developed in our country but still it is not recognize as an academic course. Also, it is not required to think that all the time knowledge will come from western. So, this is the perfect time to introduce social business in our academic curriculum. Usmita Afrose (2012) shows operating procedures and marketing implications of social business. Furthermore, identified social business is a powerful technique of creating and retaining the brand image and gaining a competitive advantage of the company's instead of corporate social responsibility (CSR). In future, social business is more effective and sustainable issue for solving different social problem in our country. Dr. ZaidiSattar (2012) stated that still the world economy is turmoil situation due to the inefficiency of capitalism. Profit maximization is the main motive of capitalism system but social business is discontinued from such selfish concept. Wimmer(2012) detected that the activities of Grameen Shakti, and to identify how a social business can change the daily lives of rural people. She perceives the role of social business to the society. EzgiYildirimSaatci & Ceyda Uper (2013) shows the clear idea about the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Social Business. Social business and CSR have much in common in that sense; both are take interest to solve the social and environmental issues. Moreover, there is the difference between two philosophies, based on their purposes, structures, targets, profit related policies, compliances issues, and shareholders' perspectives. Parisa Islam Khan (2015) emphasized on creation of value through customized marketing programs like innovative needs & wants based offerings, segment based pricing approaches, strategic partnership for distribution, building relationship with local community, use local dialect or languages for marketing communication & studies the difficult policies & procedures. Masum Billah(2015) describe that social business is looking for market-based solutions to solve the different types of social problems. Also, thought that traditional capitalism, corporate social responsibility is apparently failed to protect the interest of the poor people. But, finally research proved that social business model (like, BASF Grameen and Grameen Shakti) is benefited for the people of Bangladesh. Andrew Rebeiro-Hargraveet al.(2015),they have identified the contributing factors which are significant for evaluating performance of each market destination and selection of social business portfolio from the social point of view with maximum social impact. Jean-Luc Perron (2011) noticed that Professor Dr. Yunus developed the idea of social business much before the global economic crisis surfaced to solve the major social problem. It is a combination of entrepreneurship and selflessness, which aims to achieve social goals.
3. III.
4. Objectives of the Study
Social business is a relatively new idea. This innovative concept empowering people's lives is spreading fast. The main purposes of this study are -1. To show the structural layout of social business. 2. To compare the social business and traditional business. 3. To show the development scenario of social business in Bangladesh and rest of the world. 4. To analyze the performances i.e. social impact of social business in the context of social issues. 5. To make some recommendations for adapting the new idea of social business.
IV.
5. Limitations of the Study
In conducting this research, a primary limitation is that sufficient numerical data is not available for statistical and econometric analysis.
6. V.
7. Research Methodology
This research is descriptive in nature which has been conducted based on the secondary sources. It consists of books on social business by prof. Dr. Muhammad Yunus, different articles on social business and corporate social responsibility, case studies, working papers, The Yunus Centre Social Business Design Lab, different social business firms and other few relevant websites. Also, followed social business ventures operations in social, agricultural, health, environmental areas etc.. Statistical and econometrics analysis is not possible due to the lack of sufficient data.
8. VI. Structural Layout of Social Business
Social business is a cause-driven business. It must be financially sustainable and mission-oriented. The company must achieve its social objective and at the same time cover all costs through a revenue model. The success of the business is not measured by the amount of profit made in a given period, but the impact of the business on people or the environment. Investments in social businesses purely support the accomplishment of a social objective, and an investor should desire no financial gain. In fact, in a social business, investors/owners can gradually recover the money invested, but cannot take any dividend beyond that point. Social business is a non-loss, non-dividend Company which is created and designed to address a social problem. (Prof. Dr. Muhammad Yunus, 2007). "Social business is a powerful concept at the intersection of the social and business realms. The objective is to apply the professionalism and efficiency of the business world to solve the world's most pressing social problems. And to do so, in a self-sustaining way, providing for choice and personal responsibility for those who benefit from it." (The Boston Consulting Group, 2013).
Therefore, social business model is to provide opportunities for the investors or the business owners to make profit from their investments for their society and to create lasting effects for the marginalized. All the net profits remain within the company for further development and extent. The investor will get the principal amount back, but nothing beyond that. A company operating as a social business needs to work profitably in order to cover initial costs and to invest its earnings in the expansion of the business. In this way, their products become available for the poor. The ultimate goal is to enrich and empower people.
There are two types of social businesses whose feasibility would like to discuss about:
Type I is a non-loss, non-dividend company devoted to solving a social problem and owned by investors who reinvest all profits in expanding and improving the business. This type I business focuses on providing products or services with a specific goal of social, ethical and environmental friendly. For example, Grameen Danone, is working to solve the problem of malnutrition by selling affordable yougurt fortified with micronutrients. Grameen Veolia Water addresses the problem of arsenic-contaminated drinking water by selling pure water at a price the poor can afford. BASF Grameen will reduce mosquito-borne diseases by producing and marketing treated mosquito nets. There are many other examples -some already in operation, others in the making. Type II is a profit-making company owned by poor people, either directly or through a trust that is dedicated to a predefined social cause. Since profits that flow to poor people are alleviating poverty, such a business is by definition helping to solve a social problem. Examples of Type II social business are Grameen Bank, which is owned by the poor people who are its depositors and customers. Grameen-Otto, it will be owned by Otto Grameen trust, which will use the proceeds to benefit the people of the community where the factory is located. The difference between these two types can be stated simply -one is internally focused and the other is externally focused in its services. (Yunus, 2010) Prof. Dr. Muhammad Yunus indicated seven principles to define and categorize a business as Social:
1. Business objective will be to overcome poverty, or one or more problems (such as education, health, technology access, and environment) which threaten people and society; not profit maximization. 2. Financial and economic sustainability 3. Investors get back their investment amount only. No dividend is given beyond investment money 4. When investment amount is paid back, company profit stays with the company for expansion and improvement 5. Environmentally conscious 6. Workforce gets market wage with better working conditions 7. ...do it with joy. (Yunus, 2010) Everyone can start a social business. There is no obstacle to entry. But it owners must have the goal of resolving the social problems. The problems can be small or big. Many countries are trying with this to eliminate their social problems. The expectations are growing as well. The poor and the marginalized are benefiting from this idea. It can be started in a variety of areas which show in the figure (01):
9. B
Social business model is developing based on the economic framework, non-dividend Company to solving the social problems, such as healthcare, education, sanitation, water pollution, unemployment and environmental degradation. Several companies based on these ideas have been launched in Bangladesh. Some leading global brands such as Danone, BASF, Adidas and Uniqlo, among others, have been working with Grameen to develop some essential products such as yogurt, mosquito nets, shoes and clothes at an affordable price.
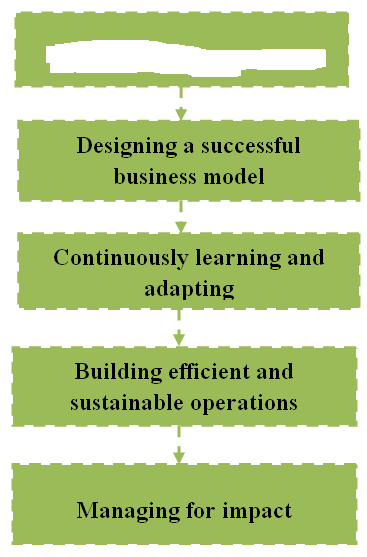
Choosing the right focus Area: All types of business entity firstly identify the needs of the customers. In this point of view, social business is not dissimilar from existing business model. Social business also concentrates its efforts to addressing the unmet social need or unsolved social problem. So, there are three factors should be considered when choosing the required right focus area -First, companies should start from a baseline of their core capabilities, goals and potential business interest; second, to develop a sound understanding of the root cause or causes of the problems not just its symptoms; third, to understand the landscape of stakeholders, regulatory environment and activities of other players. Designing a successful business model: To achieve the real impact, however, a social business must tailor its product or service to the needs, culture and local tastes of targeted population. After that, one of the biggest challenges for social business is to sell products at affordable prices to the worlds neediest -often the poorest of the poor. For removing the clash between affordability and sustainability, social business considers three differentiated pricing options. One is to charge the lowest possible price to reach people most in need. The second option, a moderate premium price, is possible if the additional value is clear. The third option is to price products differently for different customer segments, charging prices based on a customer's ability to pay. We know that, most of the poor people live in rural areas unreachable through established distribution networks. So, to succeed social business must rethink how they physically reach their target customers, adding traditional commercial channels within novative methods of distribution. Finally, for many reasons, getting target populations to buy and properly use a new social product is difficult. Due to the lack of education, customers are not aware about the value that the social business is offer. Therefore, to create demand for its offering, a social business must develop marketing that effectively reaches and communicates a clear value proposition to the target population in need. Continuously learning and adapting: Throughout the development process, the business model must be continuously monitored and adapted to ensure that it is economically feasible and delivers real social impact. This learn-and-adapt cycle can be approached in one of two ways. This "learn by doing" approach involves entering a market quickly with a small-scale prototype and gathering direct feedback i.e. take a fast mover advantage and try to introduce new ideas in the marketplace quickly. Another way, some proactive planning, market research, and refinement of the business model can minimize the risk of failure. But waiting too long poses its own risk because unless a Building efficient and sustainable operations: Social business can only be achieved long-run benefits, if it building efficient and sustainable operations. To remain viable over the long term and increase the social impact, social businesses must structure operations and partnerships effectively, hire and retain the right talent, and design operations to be as lean and efficient as possible. If it possible, then social business delivering real social impact and doing so self-sustainably.
Managing for impact: Success of social business means two things one is delivering real social impact and another, doing so self-sustainably, without the financial support of a corporate partner or outside donations. Outcomes of a social business may seem intangible or difficult to evaluate. But, clear metrics can help to quantify the impact of a social business on the target population. At a minimum, social impact should be measured along two dimensions: the impact on each beneficiary and the number of targeted beneficiaries reached. For instance, an initial analysis comparing Grameen Shakti's solar home systems to the kerosene alternative suggests that the average household with a home system reduces its carbon dioxide levels by roughly 0.25 tons per year and generates net annual savings of ?58. The firm reveals a total reach of about 1.2 million households, about 3,14,000 of which are estimated to be in the targeted population. Ultimately, increasing social impact requires scaling up the social business to maximize the number of beneficiaries reached.
We all know that the earliest form of business was barter, (the exchange of one goods for other goods without intervention of money). Then the existing business was developed i.e. we talk about traditional business which is recognized as a vehicle to earn money, to make profit. The whole idea of traditional business was built around the idea of making money. In the 21st century the corporations fail to create economic value in a way that also creates value for society by addressing its needs and challenges. No dividend is distributed to the owners. Traditional business always concerned with increasing the shareholders' value.
Social business is concerned with maximize value derived to society as opposed to the financial value delivered to shareholders. Traditional investors invest for his / her own benefits.
Social investors invest for others benefits. Most of the time employees deprived from getting appropriate salary.
It is ensure by the company, employees get wages in market rate. In the traditional business owner can bear all the capital, profit and loss.
In the social business owner can get back only the initial investment.
Till people think that social business is one kind of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). But there is huge gap between these two concepts which are given below: Social Problem: Lack of nurse: only 1 nurse for every 6,300 people. Ratio of nurses to doctors is 1:2 instead of the typical 3:1, Poor maternal and child health is a persistent problem in Bangladesh, lack of access to medical care among poor and rural populations. Social Impact: Empowerment of disadvantaged youth, Improved ratio of nurses to doctors, positive effect on maternal and child health.
10. Grameen Shakti
Relevant Social sectors: Health, Agriculture, ICT.
Nature of Product: Solar home systems, improved cooking stoves, small biogas plants.
11. Source of fund: Partnerships
Social Problem: Low living standards and unhealthy environment in rural areas, 70% of households were not connected to electricity, kerosene stoves pose high fire risk and cause eye irritation due to smoke. Social Impact: More than 8 million beneficiaries; More than 12,000 jobs created; Energy access, improved health environment, reduced deforestation; approximately 8,00,000 tons of carbon dioxide saved per year through biogas, cooking stoves, and solar systems.
12. Grameen Distribution
Ltd.
Relevant Social sectors: Health, Power, ICT Nature of Product: Variety of products: telecommunication, energy and health.
13. Source of fund: Partnerships
Social Problem: Remote Bangladeshis lack access to a variety of daily consumer products of high quality, prices often exceed customer's purchasing power.
Social Impact: Reaches 9 million households in remote areas, supplies social and normal daily consumer goods, create 9,000 jobs Grameen Fabrics and Fashions Ltd.
Relevant Social sectors: Manufacturing Nature of Product: Produce bed nets to combat malaria and dengue.
14. Source of fund: Partnerships
Social Problem: 40% of Bangladeshis are underemployed, production capacity is lacking for social products.
Social Impact: 450 jobs created, offers social services for employees, such as a day care center and educations for employees' children.
15. Sources: Own construction based on data of Particulars Company and
The Boston Consulting Group.
VIII.
16. Scenario of Social Business Impact in Worldwide
Yunus Social Business applies business approaches to the world of social development, bridging the gap between social businesses and philanthropic lenders and donors. Yunus Social Business has an onthe-ground presence in the Balkans, Brazil, Colombia, Haiti, Tunisia, Uganda, and Costa Rica where our local country teams run our two main initiatives: Entrepreneur Services and Financing.
17. Colombia
18. Name of Company
19. Area
Agriculture and Livelihoods Social Problem Faced tremendous difficulty in finding legal employment. Out of 7,53,000 housekeepers only 10% are legally employed in Colombia.
20. Way of Solution
By providing a stable source of income for housekeepers, ensuring the booking and payment for services is done under proper legal conditions that ensure the rights of housekeepers. The domestic workers enter an employment agreement including social benefits.
21. Results
The company is currently employing 250 housekeepers that service over 3,000 customers.
22. Area
Agriculture and Livelihoods Most of the families cannot afford from big supermarkets and large quantities for their daily commodities. As a result they buy from local stores affect to pay up to 40% more.
23. Way of Solution
Algramo's solution is to reduce the distribution channel, sale small quantities at reasonable price.
24. Results
Algramo fills the machines, installs them for free in small neighborhood stores, and splits the profit evenly with shopkeepers.
25. Chuculat
26. Area
27. Agriculture Livelihoods Social Problem
Colombia farmers have faced unstable conditions that prevent them from accessing markets and distribution channels.
28. Way of Solution
SachaChuculat seeks to aggregate the value chain with the producers' participation in the commercialization, sold in large retail stores. Also, producers are paid above market price and receive a profit share.
29. Results
Currently, Chuculat employs 130 families, and has established partnerships with 4 organizations.
30. Sacha Colombia
31. Area
Agriculture and Livelihoods Social Problem Armed conflicts create difficulty for distribution and lack income opportunities in the rural area's farmers in Colombia.
32. Way of Solution
This company helps the farmers go through a process of integration to become business partners in agro industrial units through a multilevel online sales platform and strategic alliances.
33. Results
With 880 farmers and partnerships with 9 organizations, they have developed a strong network of distribution, selling to over 15,000 people thus far.
34. BIVE
35. Area
Health and Sanitation Social Problem Low-income families lack sufficient access to healthcare, denial of services and medications, long waiting times, and difficult administrative procedures are a huge obstacle for the poor in Colombia.
36. Way of Solution
BIVE has created a network of over 120 health care providers that offers discount (up to 68% on the price of private providers) and immediate care with a focus on the poorest of the poor.
37. Results
The social business generates revenue through affordable membership contributions. Since inception Bive currently serves over 20,000 members in the Caldas region, many of them from low-income families.
38. Campo Vivo
39. Area
40. Agriculture and Livelihoods, Education and Vocational Training Social Problem
Rural farmers often face challenges of: low crop yields, restricted access to capital, new farming technologies, and technical assistance as well as little bargaining power for the sale of their crops.
41. Way of Solution
Campo Vivo works with groups of farmers to improve their quality of life, as well as the lives of those working in the entire production chain. Campo Vivo intervenes in the agricultural chain from production through to commercialization.
42. Results
This provides income opportunities for local farmers from vulnerable communities that lack of sufficient access to markets and networks to sell their products.
43. Uganda
44. Spouts of Water Area Health and Sanitation
45. Social Problem
About 30% or 10 million Ugandans, still faces lack access to safe drinking water. They still depend on unsafe sources such as rivers, lakes and unprotected wells.
46. Way of Solution
Spouts of water is manufacturing affordable water purification filters for households to ensure that they have constant access to clean drinking water and eliminate the cost and time incurred in boiling drinking water.
47. Results
The company is targeting households in Uganda which do not have access to safe drinking water as well as those that depend on boiling water to make it safe for drinking.
48. Sage Uganda
49. Area
Agriculture and Livelihoods
50. Social Problem
Traditional crops such as sesame often don't yield sufficient margin to sustain the livelihoods of the northern Ugandan farmers.
of Solution Sage buys the Chia at a fixed market price and exported to international and regional markets. Farmers who grow Chia Seeds earn up to 50% more than those who grow other crops.
51. Results
A higher income for the local farmers improves living conditions of the whole household.
52. Jali Organic
53. Area
Agriculture and Livelihoods
54. Social Problem
In sub-Saharan Africa, more than 40% of the population lives in poverty, and many farmers lack access to markets and the know-how to make agriculture more efficient which negatively impacts their incomes. The produce cultivated is often sub-standard, not meeting organic or ethically
55. Way of Solution
The company markets its products in the international organic died fruit market. Its main customers are export distributors, including a Japanese distributor that sells products in Russia and in Europe. They are also working with a UK based dried fruit wholesaler.
56. Results
Currently working with 150 farmer groups, the company abides by the international fair price policy, supporting small holder farmers with fair loans and prices to promote food security.
57. Adapt Plus
Ltd.
58. Area Energy and Environment
59. Social Problem
Many refugees living in Uganda lack access to fuel for cooking and heating.
60. Way of Solution
Adapt plus produces energy-saving cook stoves and fuel briquettes, ensuring a reliable supply of equipment and fuel for cooking and heating.
61. Results
The stoves and briquettes are then sold on to community retailers and directly to households in the local community. Savco Millers Ltd.
62. Area Energy and Environment Social Problem
It is estimated that over 108 tons of plastic waste are generated in Uganda every day, yet the recycling capacity is less than half that amount.
63. Way of Solution
Savco Millers purchases plastic waste from collectors at a premium priced recycles it into new products like grow bags for trees, construction sheets and waste collection bags. Their products are then sold back to the local community at affordable prices.
64. Results
Savco Millers aims to significantly reduce the environmental impact of plastic waste by collecting, recycling and selling plastic waste.
65. Afard Holdings
66. Area
Agriculture and Livelihoods Social Problem Lack of employment opportunities and low household incomes causes poverty and food insecurity for many children in rural Ugandan communities.
67. Way of Solution
The business runs a tractor hire service, where farmers can rent tractors at affordable prices. Farmers are offered a number of flexible payment schemes including the option to pay 50% of the hire costs after their produce has been harvested.
68. Results
The business provides equipment to local farmers, helping them farm more land and increase their income, improving the lives of their families and their local communities.
69. Awamu Bio Mass
70. Area
Energy and Environment
71. Social Problem
Marginalized communities in Uganda often use high cost, inefficient and in many cases dirty cooking solutions. This can cause health issues and pollutes the environment through increased CO2 emissions.
72. Way of Solution
Awamu targets households in peri-urban and rural settings that use biomass for cooking through established structures like Farmers groups, SACCOs, church groups and local women groups.
73. Results
It has designed an energy efficient stove that is 90% smokeless, reduces cooking time by 50% and uses plant biomass. Brazil
74. Moradigna
75. Area
76. Health and Sanitation Social Problem
Nearly, 6% or 11 million people live in slam in Brazil. People live in poor, unsanitary conditions, and houses often do not meet legal regulations.
77. Way of Solution
Moradigna provides services reform housing structures, diagnosing the problem and providing rebuilding, design, and labor to properly regulate living conditions.
78. Results
Low income peoples are getting safe conditions to live in, the ability to pass safety and hygiene regulations, and to prevent the spread of diseases.
79. Assobio Area Energy and Environment
80. Social Problem
Brazil nowadays has lost approximately 85 million hectares of native forest due to deforestation.
81. Way of Solution
Assobio works together with the local community and involves them in the process and maintaining the forest and provides education and training opportunities for the local community.
82. Results
Companies receiving public tenders are legally obliged to reforest the fraction of rain forest they use.
83. Balkans
Enterprise Rizona Area Agriculture and Livelihoods
84. Social Problem
Negative trade balance, still the poverty rate is nearing 30%, and with over 60% of youth facing unemployment faces by Kosovo.
85. Way of Solution
Rizona is involved in the collecting, selecting, processing and conservation of different vegetables from over 100 smallholder farmers, processing them so that they are ready for export.
86. Results
100% of the product is exported which generate foreign revenue. Also create opportunities for access to market and incremental income.
87. Udruzene Area Education and Vocational Training Social Problem
Unemployment rate in Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH) has reached the level of 42,9% in 2015 from which 26.8% are women.
88. Way of Solution
Udruzene's uses knitting as a way to help women who have suffered from war, violence and social marginalization in the past by providing education and professional training on Handicraft products.
89. Results
Women's are economically and psychosocially empowered. Create employment opportunities for women.
90. Seniors Home
91. Area
92. Health and Sanitation Social Problem
Seniors in Albania represent 9% (270K) of the total population expecting to rise to 15% in 2020. The situation is expected to get worse. Even today seniors in Albania often lack of access to sufficient quality elderly care.
93. Way of Solution
Seniors Home provides high quality daycare and residential services, food, daily activities, physical therapy and medical assistance for improving quality of life of senior citizens in Albania.
94. Results
Seniors Home already has provides this facilities to the 28 clients. Also, offers employment and training for young nursing professionals. Saint George Organic Herbs Farm (SGOV)
95. Area
Agriculture and Livelihoods
96. Social Problem
Soil erosion and irresponsible harvesting have drastically reduced the quantities available and traceability of the products is becoming increasingly difficult.
97. Way of Solution
The farm owns a seedling nursery to ensure quality of inputs and produces sustainably-grown organic herbs for local and international traders and processors of herbal oils.
98. Results
This provides additional income opportunities for local farmers. Once being organic-certified, it will open access to international and local markets.
99. Tunisia
100. Biopam
101. Area
102. Agriculture and Livelihoods
103. Social Problem
Unemployment, unstable and unsecure sources of income is the main problem because the majority of employment opportunities are agricultural, low-paying and seasonal.
104. Way of Solution
By developing an organic herb value chain of production, in order to meet the growing international demand for organic dried herbs.
105. Results
It provides sources of stable and higher-than-average income for its female and out-growers.
106. Centre
107. Results
CIFEA includes the local people in the organic honey processing system after providing training facilities that create the employment opportunities.
Cluster Laitier Area Agriculture and Livelihoods Social Problem Annual average loss around 30% of their production due to the lack of formal milk collection system which negatively impacts their profits.
108. Way of Solution
By providing access to a formal, regulated, and daily collection processes, and to regular distributions of composed fodder.
109. Results
Finally, increase the profits of small livestock farmers.
110. Significance of Social Business
The business concept is still under development stage in Bangladesh as well as over the world. However, day-by-day it is developing. So, for getting the ultimate social impact, it takes some time. Nevertheless, it has already brought following welfare implications for the society.
Poverty Alleviation: Poverty alleviation includes the strategic use of tools such as education, economic development, health and income redistribution to improve the quality of life of the world's poorest by government and internationally approved organizations. Last 60 years, the global economic growth and financial development is massive, however, we see little progress in global poverty reduction. To achieve the goals as set out in the UN MDGs. It is possible through the social business because existing capitalism system believed poverty is alleviated by using financial aid but professor Yunus believed that poverty is alleviated by social business. The ultimate goal of social business is to alleviate the poverty. This goal can be achieved in two ways. Type I social business focuses on lift the quality of life of poor by providing their basic products or services with an affordable prices. This basic product indicates shelter, cloth, food, health and education etc. Type II is a profit-making company owned by poor people, either directly or through a trust that is dedicated to a predefined social cause. Therefore, this type of social business making them as self-entrepreneurs.
Create Employment and income Opportunities: Social business have already recognized that it is concerned with the basic needs of the poor. In that reason poor people get priority in the recruitment process of a social business company. These poor people are involved in supply, production and distribution channels. As a result, social business creates huge employment and income opportunities.
Eco-friendly Business: Eco-friendly means which is not harmful for environment. Eco-friendly products prevent the air, water, soil and other pollution. There is an interdependent relation between eco-friendly and sustainable development. Since sustainable development is that type of development which meets the needs of the current without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Originator of social business Professor Yunus develops seven principles on social business, 'Eco-friendly and Sustainable Business' is important one. During the study we have observed that Social Business entrepreneurs are concerned about the environment that is why they produce environment friendly products like, Grameen Danone Foods. It has an environmental aspect: solar energy is used for heating up the water which is used for cleaning the installation and pre-heating water for the main boilers also packing of the yoghurt is fully biodegradable. Reduce Aid Dependency: Aid dependency refers to the proportion of government and private spending that is given by foreign donors. Most of the time, donations money is not spent in properly. In this reason professor Yunus developed an alternative solution i.e. social business. Suppose, a multi-national company donates a nations' for decreasing the poverty but question is how many times that company donates to solve this problem. From the concept of social business, we see that an individual investor or a company can invest in a social business after establishing a social business, investing company only get back their investment. Profit is retained for continuing business. Finally, a business is established in own way. So it is clear that social business reduced the aid dependency. Mobilize private sector resources: We know that private sectors capital can generate profit for its owner. Social business ideas bridge the gap between private sector resources and social problem. But, if the government wants, then it is possible to solve the social problem of a country by using the private sector's resources. Those companies invest in social business that companies will get government tax exempt for a certain time period; it could be before establishing a particular social business. So, there is lot of way to mobilize the private sector resources. Overcome charity approach to development: Professor said that -"A charity dollar has only one life; a social business dollar can be invested over and over again." From the above quoted, charity approach is work only for a short period of time. It has no sustainability in the context of development like a social business. While investors may recoup their investment, all profits are reinvested into the same or other social business. This is a non-stop process for solving the social issues. So, social business united the dynamism of traditional business with the social conscience of charity.
111. X.
112. Challenges of Social Business
Social business is the term directing to solve the social problem in a sustainable way. It is obviously replacing Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and charity. Although there are a number of countries doing social business in successfully yet it has some challenges which are given below -
113. B
Issue of motivation: This is a common phenomenon in traditional business, every investor's expected return from his or her investment but professor Yunus argues that a social entrepreneur involved or doing social business from his / her selfishness or social desire motives not profit motive. Still this is a big question; merely social purpose is enough to motivate a social entrepreneur to go for social business.
Financing problem / lack of start-up finance: of capital is a big constraint for starting a social business for many social entrepreneurs. Since many developments co-operation actors prefer to support only the social purpose of a social business, while making sure that their money is not used for business profit. This separation may be impossible for a social entrepreneur to achieve. Another, problem of financing in social business, banks often perceives social businesses as risky because they involve unconventional business models. Problem of Regulatory Framework: In the absence of a clear regulatory framework, anyone could claim to run a social business. The problem, however, in establishing such a regulatory framework is that what is considered "social" is context-dependent. For example, some communities may see the provision of clean water, albeit at a cost, as a noble cause, while others see it as contradicting an inherent human right -access to drinkable water. Performance measurement criteria: Social business is not so much dissimilar from traditional business which already explained. We know that there are so many techniques develop to measure the performance of traditional business. But it is still not clear how to measure the performance of social business. Because, main goal of social business is to achieve social objectives.
114. Adaptability and Time frame problem:
There is a big question; is it work only poor country? This is true in developing countries, there are lots of research work have already been done. But, still they are not adopt the social business for solving their social problem. Then again, social business has not dramatically solved the social problem. It can take tome 5, 10 or even 20 years.
115. Absence of Universal Social Reporting Standard:
Assessing the social impact of businesses tends to be resource-intensive and complicated, not only because of potential time lags between interventions and impact, but also due to the absence of universal social reporting standards. Without universal standards, it is impossible to compare the net impact of different social businesses, in particular because of the potentially large number of positive and negative side effects that should be taken into account. It is critical that all positive and negative outcomes be considered to avoid unintended side effect and to measure a venture's net social return on investment.
116. XI.
117. Recommendations
The main purpose of this study is to show the structural progress of social business and how social businesses diminish the social problem of Bangladesh and rest of the world. On the basis of the analysis, we make several important suggestions for improving the effectiveness of the social business model. Such as -? To establish an effective social impact measurement techniques or system so that a huge number of stakeholders can agree to take the position of this system. ? Still social business is in the elementary stage. So, there is an adequate research works is needed to find out the real social problems and convert them to a business model and also for enjoying long-term benefits. ? To build a legal, regulatory and fiscal framework is required to bring the clarity of the social business between the investors and stakeholders. ? We know, education is the most powerful weapon which can change anything in a positive way, so use education as a key strategy for developing a culture of social business like a traditional business. ? The government can be a major player for boost-up the social business. If the government and private organizations work with jointly then it would be possible to solve the different type's social problem especially in the developing and under developing countries.
XII.
118. Conclusion
Traditional philosophy is that business people have all the right to make money, however, at the same time they also have some responsibilities for solving social problems. The formula of social responsibilities has not any sustainability for mitigating social obligations. The finding shows social business has a structure which is in progressive trend also it contributes to human development by enlarging people's choice in an economically, environmentally and socially sustainable way. Side by side there is dissimilarity in the context of financing and return of investors from traditional business. Nevertheless, the development of social business is one of the newest paths which teach us how to be selfless in a self-centered world and it has the power to reform the society in many aspects specially, poverty free, unemployment free and carbon free.

| Traditional business | Social business |
| Profit maximization. | Social benefit maximization. |
| Dividend is distributed to the owners. |
| Global Perspective | ||
| VII. Scenario of Social Business Impact Bangladesh | ||
| Name of Company | f) Comparison Between Traditional Business & Social Business Facts | |
| Relevant Social sectors: Health | ||
| GrameenDanone Foods | Nature of Product: Yogurt fortified with micro-nutrients | |
| Ltd. | Source of fund: Partnerships | |
| Social Problem: 56% of the worlds' under the aged of 5 year's children suffer from | ||
| moderate to severe malnutrition. The long-term effect of malnutrition cause economic | ||
| 2016 | underdevelopment. Social Impact: Reduce poverty by including local communities in all stages of the | |
| Year | business operations. Also, it has created 1,600 jobs opportunities. Relevant Social sectors: Health | |
| 12 Volume XVI Issue VIII Version I ( ) B | Grammen Veolia Water Ltd. BASF Grameen Grameen Intel Social g) Comparison Between Csr & Social Business Nature of Product: Delivering drinking water by tap point network Source of fund: Self-Financed Social Problem: 37 million people of Bangladesh are at risk of arsenic poisoning. Social Impact: Reduce the arsenic poison by providing pure drinking water. Employment: employees 21, water keepers 45, and jar distributors 10. Relevant Social sectors: Health Nature of Product: Long-lasting (2 to 5 years) insecticide-treated nets. Business Ltd. | |
| Global Journal of Management and Business Research | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) It is profit sharing. In case of CSR, fund is aside from the small portion of the profit. The effect of CSR is one-time. CSR is used to build a corporate image. It is not sustainable. The ultimate objective of CSR is making profit. CSR is a strategy within a company. It is the legal / compliance obligations for any organization. GrameenYukiguniMaitake Ltd. Relevant Social sectors: Agriculture It is non-dividend. Social Business (SB) In case of SB, fund is making from any individual, any company, even government. The effect of SB is longer period. SB is used to solve the any social issues or problem. It is sustainable. The ultimate objective of SB is maximizing the social benefits. SB is itself a company. Compliance of a social business is "Selflessness" to engage in a social problem solving. Nature of Product: Cultivation and processing of large and small mung beans. Source of Fund: Partnerships Social Problem: Underemployment, poverty, and malnutrition in Bangladesh, women face hardship, lack of knowledge in the agriculture sector. Social Impact: Create more than 18,000 jobs. On average, farmer's income increased 20% over last year's levels. Agriculture efficiency increased from 800 kilograms per hectare to 1,200 kilograms per hectare. Grameen GC Eye Care Hospital Relevant Social sectors: Health Nature of Product: Three hospitals offering general eye examination and special surgery. Source of fund: Partnerships | |
| Social Problem: 7,50,000 blind people, 2,50,000 people with ametropia (low vision) | ||
| © 2016 Global Journals Inc. (US) 1 | ||
| 2016 |
| Year |
| Volume XVI Issue VIII Version I |
| Global Journal of Management and Business Research ( ) B |