1. Introduction
ourism is circulation of people who travel to or stay in places outside their home country (their usual place of residence and/or work) for short periods, usually no longer than a year, and for different purposes such as leisure, business, or any purposes other than formal employment (UNDESA, 2010; UNWTO, 2013). Tourism is a major constituent in the economic development strategy (WTTC, 2012). It has become one of the largest socio-economic and social sectors registering rapid growth worldwide (Goeldner and Brent, 2012;WTTC, 2015); and accounts for 10% of global gross domestic product (GDP); plays significant role in accelerating development and eradicating poverty (Zortuk, 2009;Meriague, 2014). Vellas (2011) stated that it is newly emerging industries and became an increasingly important source of income, employment and wealth in many countries. On the other hand, various factors have been affecting sustainable development of the tourism industry worldwide. According to Philip (2017) factors affecting tourism industry development may be either internal or external. External factors like weather, safety, access to amenities, peace, and security may affect the development of the tourism industry (Becken, 2010). Likewise, internal factors like inadequate infrastructures, weak human resources, low marketing and promotion strategies (Mekonen, 2016;Selemon and Chiranjib, 2018), and weak linkage with international organizations can hinder the development of tourism industry in a given place (Tadesse, 2015;Yimer, 2016). Rachel and Richard (2009) stated that management decisions are not worth the paper they have being written on and decisions have being not implemented. Lack of integration and recognition of tourism on political agendas have also contributed to the weak development of tourism industry (Dodds, 2007a;Telfer and Sharpley, 2008). Lack of coordination and commitment between government bodies, an absence of stakeholders involvement, weak communication between authorities have been hindering the sound enough development of the tourism industry (Ardahaey, 2011;WTTC, 2012;Yimer, 2016). Although Ethiopia possesses numerous natural, religious, historical, manmade and cultural tourism attractions, economic contribution and its potential are incomparable (Ali, 2017); the sector's contribution to the nation's GDP was 4.1% in 2015 which is very low (WTTC, 2016). Even though Ethiopia has known with an ever increasing international tourist flow, the country is one of the lowest tourist flow benefit recipient countries in Africa (MoCT, 2012; UNWTO, 2012). There is a shortage in number and type of tourist facilities at existing and potential tourist destinations and vicinities; interpretations and presentation of tourist attractions are not based on credible facts and knowledge (Ali, 2017). Handicrafts, local creative products, performing arts and entertainment services, which can help to lengthen the stay and increase spend of visitors at every destination, are not offered in sufficient variety, quantity and quality (Tadesse, 2015; Yimer, 2016). Moreover, there are inadequate trained human resources (Ali, 2017;MoCT, 2012). Similarly Gambella People's National Regional State is one of the beautiful tourism destinations of the country which has being located in Southwest of Ethiopia. It has a wealth of natural, non-natural, historical and cultural resources (Selemon, Chiranjib, and Alemken, 2019). However, the development of the tourism industry in the region is in the infant stage. According to MoCT (2012) visitors' survey, few tourists have been visited the Gambella Region; and also the region has not been listed under the influential tour and travel operators' package. There are various factors hindering the development of the tourism industry in the region. Nevertheless, a limited study has done in identifying factors hindering the development of the tourism industry in the region. Hence, the current research addresses the above-stated problems and contributes to the tourism industry development in the Region.
2. II.
3. Research Methodology a) Description of the Study Area
The study was being conducted from June/2018-April/2019 in Gambella People's National Regional State. Gambella People's National Regional State is located in the South-western part of Ethiopia about 777 km away from Addis Ababa, the capital city of Ethiopia. It has being situated in the lowlands of Baro-Akobo River Basin between latitudes 6 0 22' to 8 0 37' North and longitudes 33 0 10' to 35 0 50' East. It has a total area of approximately 34,063 km 2 of land. The region borders with Benishangul Gumuz and Oromiya regions to the North; Southern Nations, Nationalities and People's Regional State (SNNPRS) and the Sudan Republic to the South; Oromiya and SNNPRS to the The population of this study comprises three zones of Gambella region with their twelve woredas (Gog, Abobo, Jor, Abol, Dimma, Jikaw, Makuey, Lare, Wanthowa, Akobo Godere, and Mengeshi Woredas. It also involves Itang special woreda and Gambella Town Administration. In this particular study, the non-probability sampling technique (purposive sampling) was being employed to get relevant data from the respondents. Accordingly, key informants from 3 zones (n= 15), 13 districts (n= 65), Gambella National Park office (n=5), Gambella Culture and Tourism Bureau (n=5), Gambella Tourism Organization Office (n=5), Gambella Culture, History and Heritage Research Directorate (n=4) and Gambella Government Communication Office (n=4), altogether 103 respondents were purposively selected. Selection criteria were: i) their position in a zone, districts or kebeles, ii) their level of knowledge and experience to the tourism industry iii) the most senior experts and iv) the most relevant individual who can give crucial data to achieve the objectives of the research.
4. c) Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods should be stated clearly. Properly planned data collection method provides a clear overview of what tasks would be carried out, who will perform them, organize human and material resources, and minimizes errors. There are 3 zones and 13 Woredas to conduct an inventory of natural tourism potentials of the Gambella Region. Since it is difficult for a single person to collect data from those zones and Woredas, it is crucial to involve data collectors. Thus, three data collectors from Gambella Tourism Organization were purposively selected. The selection criteria were: a) they are experts in Gambella Tourism Organization, b) they know better about tourism potentials of the Region, c) they can easily communicate and gather data from the woredas administrators and senior experts, and d) they are our primary stakeholders in this particular study. Hence, the discussion was held for this research how to collect data from the 3 zones and 13 woredas. Preliminary field visitation and data collection was being done together. Gambella Tourism Organization Office experts further gave training for other woreda level data collectors as a necessity. They gave full orientation for woreda level data collectors before they were left alone. In all circumstances, monitoring, seldom field visit, cross-checking and verification were done to ensure the reliability of the data. According to the scheduled plan, in-depth interview using open-ended questions has been held with purposively selected key informants. Respondents were being given the opportunity to express their ideas, opinions, feelings, and knowledge about factors hindering tourism industry development in the region as well as their respective zones or woredas. Furthermore, the research crew was also made field observation through recording important information, note taking, photo camera capturing, etc. regarding natural tourism potentials of the region. On the other hand, secondary data sources (published documents, articles, books, unpublished data, archives, brochures, etc.) were being referred for the further clarification of the data.
5. d) Data Analysis
Qualitative data was being analyzed in meaningful content description whereas quantitative data was being analyzed in numerical values. The data gathered first edited, categorized, arranged and organized before encoding into the software. Frequency and percentages were calculated using SPSS software version 20 and charts and graphs were used to show results. Text explanations and descriptions used in the case of the qualitative data analysis. Likewise, data collected through field observation were being analyzed in a content descriptive way to relevant meaning and summarization.
6. III.
7. Results and Discussions a) Demographic Characteristics of the Respondents
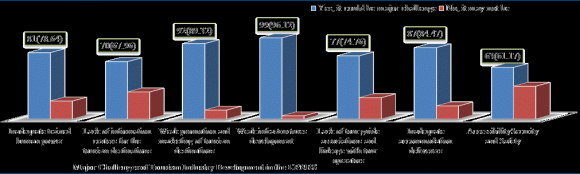
In this particular study, demographic characteristics like sex, education level, income levels, age categories, as well as the marital status of the respondents were being observed. As table 1 shown below about 83.5% of the respondents were males. Concerning education level, most of the respondents were educated one (first-degree holders) (74.76%), and 22.33% of the respondents were diploma holders. Most of the respondents (68.93%) were between the ages category of 26-35 whereas a few respondents (6.8%) were in the age interval of 46-55. Concerning marital status, most of the respondents were being married (95.15%) (table1). Even though Gambella People's National Regional State has endowed with enormous tourism potential, its tourism industry development is relatively in the infant stage. The region is not benefited from tourism industry sector as expected and compared with existing tourism potentials. Different factors have been hindering the development of the tourism industry and maximizing benefits from the sector. The region has received very few visitors flow which results in less contribution to economic growth from the tourism industry. According to the findings of this study, the main factors challenging tourism industry development in the region were being discussed below (Figure 2). Tourism industry needs specialized, trained and committed human power for its sustainable development in a particular area. Because, it has its terminologies, principles, approaches, rules, guidelines, code of conducts, and so on. Inadequate specialized human resources in a specific tourism sector means its development in that area is under question. This phenomenon is also visible in the Gambella Region in tourism industry related sectors. About 81(78.64%) of respondents presented that tourism industry sectors have inadequately specialized, trained and skillful experts. It is the fourth-ranked major challenge which is hindering tourism industry development in the region. In the zonal and woreda levels, there is lack of specialized expert who contributes That is why tourism industry development in the region is in the infant stage.
8. ii. Lack of Information Centers for the Tourism Destinations
Information centers play a vital role in attracting visitors to the destinations and contribute to the tourism industry development. It may be offices, agencies, information desks in the hotels, recognized individual/groups. They provide valuable and brief information for visitors regarding destinations in the area. Among the respondents, about 70(67.96%) indicated that lack of information centers for the tourism destinations in the region has contributed to the low flow of international and domestic tourists to the region. Even in the Gambella town, the capital town, there is no information center. Hotels, guest houses, and pensions are not committed and delivering information about tourism attractions of the region. Hence, lack of information centers in the regional, zonal and woreda level is the sixth-ranked major constraint of tourism industry development in the region.
9. iii. Weak Promotion and Marketing of Tourism Destinations
Strong promotion and well-designed marketing strategy is the core activity in the development of the tourism industry. Efficient promotion can attract various visitors from the different corners of the world. Welldesigned tourism product marketing strategies ensure sustainable visitors flow to the destinations and make the area specific product to being known by the influential visitors. However, there is a weak promotion of existing tourism potentials and weak marketing strategy in the region. In support of this idea, about 92(89.32%) of the informants focused that there are weak promotion and marketing strategies. In spite of some promotion activities by the concerned regional offices, the tourism potentials has not yet promoted as its marvelous tourism potential. The region has being called that "the desert paradise" due to its attractive tourism potentials (lakes, jungles, forests, waterfalls, rivers, wildlife resources, cultural resources, historical sites, and non-natural attractions). Even though concerned regional government offices have been making undeniable efforts (promoting through flyers, brochures, tourism day celebration, special events, etc.), weak promotion and marketing strategies have held the second major hindering factor of tourism industry development in the region.
10. iv. Weak Infrastructures Development
Infrastructures development is the backbone in the process of tourism industry development. Every tourism destination should be accessible to be visited by different visitors, explorers, university students, researchers, environmentalists, conservationists, etc. Without improved infrastructure facilities, a certain tourism potential site could be abandoned as an insignificant tourism product. About 99(96.12%) of the informants underlined that weak infrastructure development is unresolved and the first-ranked major constraint of tourism industry development in the region. Most of the tourism destinations in the region are inaccessible for visitation and requires a long journey on foot. Even there is a lack of trekking routes, roads, campsites, resting places, accommodations, viewpoints, etc. on the way to the destinations. Furthermore, it needs the installation of electricity, water availability, communication opportunities, and accommodation centers.
11. v. Lack of Tour Guide Associations and Linkage with
Tour and Travel Operators Visitors can't communicate with all local community and ask information about the tourism destinations of the specific place. Similarly, all local community; even all experts can't make linkage with tour and travel operators as well as visitors. Hence, the tourism industry needs bridges between visitors and local community or potential tourism destinations. Recognized and certified local tour guide associations are "ambassadors" and can serve as representatives of the local community, region, state, local culture, and so on. They provide valuable and worthy information for visitors and attract different visitors to destinations through promotion and communication with an influential tour and travel operators. Nevertheless, about 77(74.76%) of the respondents stressed that there is no tour guide association at regional, zonal as well as woreda level in the Gambella region. A lack of tour guide associations has resulted in lack of linkage with a huge tour and travel operators in Addis Ababa, the capital city of Ethiopia. Besides to this, no tour and travel operators have listed the region in their travel circuit as major tourism destination area and have limited intention to work in this region due to lack of tour guide associations, standardized accommodation deliverers, weak promotion and marketing strategy. According to the findings of this study, lack of tour guide associations IV.
12. Conclusion
Tourism industry plays a central role in the economic development. Although Ethiopia is known for its considerable tourism industry development potentials, the sector's contribution to economic development is unmatched due to different internal and external factors. Likewise, Gambella Region has endowed with various tourism potentials, numerous factors have been hindering the tourism industry growth. Constraints like weak infrastructures development, inadequately trained human resources, lack of local tour guide associations, an absence of linkage with tour operators, lack of information centers, weak promotion of tourism destinations, and inadequate accommodation deliverers are the major unresolved hindering factors of tourism industry development. It requires contribution, integration, cooperation, collaboration, commitment and playing the significant role of multiple stakeholders to ensure sustainable tourism industry development in the region. Therefore, the first activity to enrich tourism industry development is improving infrastructures (roads, accommodation deliverers, campsites, water facilities, internet cafes, telecommunication, bank services, and electricity) to the tourism destinations with the contribution of multiple stakeholders. To install standardized accommodation deliverers (lodges, resorts, hotels) discussing and reaching to consensus with capable enterprises like Kurfitu Resort, Paradise Lodge, Haile Resort, Planet Hotel, Buska Lodge, Turmi Lodge, Simien Lodge, Eco-Omo Lodge, etc. is vital activity. The other activity in to develop the tourism industry in the region is effective promotion and marketing of available tourism products. It involves developing and disseminating different brochures, flyers, guidebooks, websites, using the internet and social media, arranging programmes in Medea, forming school conservation clubs, and workshops. To attract both international and domestic visitors, making a connection and communication with tour and travel operators like Ethiopian Tour Operators Association (ETOA), National Tour Operation (NATO), Four Winds Travel and Tour Agent, Awura Tours, Alpha Tour, and Travel, etc. is fruitful activity. Local tour guide associations shall be organized to promote existing tourism potentials and linked with these tour and travel operators to attract international visitors as wells to put Gambella Region under the travel circuit of different tour and travel operators. Furthermore, available tourism potentials of the region should promote wherein big hoardings, billboards, posters, photographs and travel desks being placed at selected transit points, and hotels/resorts. Teasers and Trailers must be designed to tease the travelers and tourists through various advertisements include CD/DVD. Collaterals and posters must be attractive and distributed free of cost to the hotels, resorts, restaurants, shopping arcades, supermarkets as well as tour operators for free promotion of tourist attractions. Use the internet to increase the visibility of tourism potentials of the region to exchange information and expertise by developing web pages, social networking sites like/Facebook, WhatsApp, Google+, LinkedIn, yahoo groups, and maintaining of e-mail lists current.
V.
13. Recommendations
? Proper Infrastructures need to be developed in ecofriendly starting from Gambella town to major tourism destination sites with the integration of multiple stakeholders. ? Potential promotional and marketing strategies being developed and adopted.
14. vi. Inadequate Accommodation Deliverers
Accommodation or services deliverers are one of the vital elements in the tourism industry development. However, almost there is no standardized accommodation or services deliverer, particularly in zonal and woreda level. On behalf of this explanation, about 87(84.47%) of the respondents pointed out that inadequate accommodation delivers the third restraint of tourism industry development in the region. There are very few standardized accommodation deliverers at the regional level (Gambella town, capital town); namely Baro Gambella Hotel, Tadesech Hotel, Andnet Hotel, Midregenet Hotel, Galaxy Hotel, Dessie Hotel, Solomon Debebe Hotel, Holy day Hotel, Giwa Hotel, Mobil Hotel, Asir Aleka Hotel, Tirupati Hotel, Fana Hotel, and Alazar Guest House. But, if there is high tourist flow from the different corners of the world to the Gambella Region, the existing services deliverers cannot accommodate and fulfill visitors' interests.
15. vii. Accessibility, Security, and Peace
Gambella Region is accessible through air transport (two times per day) and land transport from Addis Ababa (Capital city of Ethiopia) to the Gambella town (capital town of the region). Nonetheless, about 63(61.17%) of the key informants stated that the accessibility from the regional, zonal and woreda towns to the different tourism destinations is very poor. Some of the tourism destinations are inaccessible for higher institution students, researchers, explorers, and visitors and requires time-consuming journey on foot to reach attractions. On the other hand, informants pointed out that the region is a source of peace and security in spite of its poor accessibility to the tourism destinations.
? Information centers and local tour guide associations being organized in regional, zonal as well as woreda level.
Our heartfelt thankfulness goes to Research Directorate, Gambella University for financial support. Our deepest gratitude also goes to Mr. Sisay Befikadu, Mr. Deribachew Shewalem and Mr. Pal Gnack (Gambella Tourism Organization Office staffs and our primary stakeholders in this particular study) and Mr. Aychiluhim Aydefer (Gambella Culture and Tourism Bureau expert) for their support in data collection, cooperation and forwarding valuable and constructive ideas while conducting this research. At the end we are also grateful to our key informants for so generously sharing their time, for contributing valuable and constructive information for this work.
| Factors Hindering Tourism Industry Development: Gambella People's National Regional State, South | |||||||
| West Ethiopia | |||||||
| Sample Categories | |||||||
| No. | Variables | Regional officials* | Zones officials ** | Woredas officials *** | Frequency | ) Percentages (% | |
| Male | 20 | 10 | 56 | 86 | 83.5 | ||
| Sex | Female | 3 | 5 | 9 | 17 | 16.5 | |
| Master | 3 | - | - | 3 | 2.91 | ||
| Education Levels | degree | ||||||
| Bachelor | 20 | 15 | 42 | 77 | 74.76 | ||
| degree | |||||||
| Diploma | - | - | 23 | 23 | 22.33 | ||
| 18-25 | - | - | 6 | 6 | 5.83 | ||
| Age Categories | 26-35 | 23 | 8 | 40 | 71 | 68.93 | |
| 36-45 | - | 5 | 14 | 19 | 18.45 | ||
| 46-55 | - | 2 | 5 | 7 | 6.8 | ||
| Marital Status | Married | 22 | 16 | 60 | 98 | 95.15 | |
| Single | - | - | 5 | 5 | 4.85 | ||
| Income Levels | 2000-3000 | - | - | 22 | 22 | 21.36 | |
| (in ETB) | 3000-400 | - | 5 | 34 | 39 | 37.86 | |
| >4000 | 23 | 10 | 9 | 42 | 40.78 | ||
| Factors Hindering Tourism Industry Development: Gambella People's National Regional State, South |
| West Ethiopia |
| and linkage with tour and travel operators are the fifth- |
| ranked main constraint of the tourism industry |
| development in the region. |
| Year 2019 |
| 30 |
| Volume XIX Issue I Version I |
| ) |
| F |
| ( |
| Global Journal of Management and Business Research |
| © 2019 Global Journals 1 |