1. Introduction
ot of surveys have been done till now and each explains how drastically working environment and culture changed in last two decades. In an organization where people used to be more dependent on manual labour, obsolete machinery and out of phase equipment, have been upgraded in these last two decades due to LPG (Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization) policy adopted by India in 1991. Strict competition provided by foreign firms forced Indian counterpart to become more efficient and productive considering Human as equally important resource than the raw materials itself. India realized its' potential to compete among foreign counterparts using human resource development and succeeded immensely from these initiatives. Initially adopted by private firms, now HRD has been given special place in Public sector enterprises as well. For an organization combination of young and experienced employees is highly essential but now -a-days the trend of "rolling stone" is at helm due to many fall backs mainly employees' happiness which sometimes causes inexperienced majority work force in an organization and hence inefficiency and reduced productivity. Happiness, a qualitative term, were not given much importance in the decades before LPG but if analyzed properly, then we can easily pick out some causes like lack in "opportunity of opportunities" which increased immensely after LPG and creates millions of job and hence ones' pursuit of happiness started due to comparison to others' . If an organization wants its' employees to work for longer period then they need to understand "employees' satisfaction" which comes from qualitative goods (immaterial / non-fiscal) with quantitative goods (fiscal). An organization has to learn utilize human resource with material resources to enhance productivity and efficiency.
Generally, in PSU it is well known that younger generation frequently quit and switch to other firms as working environment in may PSUs in India still exercise feudal culture of hierarchical hegemony which forces them to quit the job and at times completely switch the profession and many turns towards doing master of business management hoping to become entrepreneur (own a profession of no gagging or hegemony).
2. II.
3. Literature Review
Job satisfaction is the feeling of self achievement aroused due to sense of comparison. Sense of achievement generally comes when individual compare themselves with their counterpart, say employees compare with the employees of other organization and so on. Parity, in the sense, may make people (or employees) feel satisfied (or job satisfied). Organization if wants their employees to be more satisfied with their work then they have to update themselves with the information of other organizations' work ethics / culture and accordingly inculcate those in theirs'. Upheaval in work culture /ethics in recent decades made many organizations lag behind others especially PSUs or government owned organizations w.r.t their private counterparts who are more modernized or updated as far as work culture /ethics, equipment, management committee and other facilities (fiscal / non-fiscal given to employees) are considered. Many aspects consist in work ethics / culture and each have significant importance for employees' satisfaction.
4. L
Human resources management practices such as pay practices, job training and supervision enhances job satisfaction of employees and so turnover of company. Correlation among all these variables are well highlighted and analyzed by Hamdia Mudor and Phadett Tooksoon ,2011". Autonomy of performing tasks, increased communication with co-workers in work place reflects in higher job satisfaction and which is always a part of High Performance Workplace Organization (Thomas K. Bauer, 2004).
With the recent change in work culture across the world and in general more influenced private sector all over the world, Public sector undertakings have been seen lagging behind as far as modern work ethics / culture is concerned. However, when PSUs tried to compete with their private competitors, they focused on productivity and so clients' satisfaction but to achieve that they need to change or adapt to the modern new work ethics and culture suddenly from feudal culture they had been following for decades which in actual compelled many employees feel uncomfortable to adapt to and so caused occupational stress and lesser efficiency in their work.
Interrelation among Job satisfaction, occupational climate and occupational stress is well analyzed by K.K.Jain, Fauzia Jabeen, Vinita Mishra and Naveen Gupta, 2007.
Job satisfaction has been defined as a pleasurable emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one's job; an affective reaction to one's job; and an attitude towards one's job. We can argue that job satisfaction is an attitude but researchers should clearly distinguish the objects of cognitive evaluation which are affect (emotion), beliefs and behaviors. This definition suggests that we form attitudes towards our jobs by taking into account our feelings, our beliefs, and our behaviors. Job satisfaction is not the same as motivation, although it is clearly linked. Job design aims to enhance job satisfaction and performance; methods include job rotation, job enlargement and job enrichment. Other influences on satisfaction include the management style and culture, employee involvement, empowerment and autonomous work position. Job satisfaction is a very important attribute which is frequently measured by organizations. The most common way of measurement is the use of rating scales where employees report their reactions to their jobs. Questions relate to rate of pay, work responsibilities, variety of tasks, promotional opportunities, the work itself and co-workers. Some questioners ask yes or no questions while others ask to rate satisfaction on 1-5 scale (where 1 represents "not at all satisfied" and 5 represents "extremely satisfied").
Geeta Kumari and K.M.Pandey [10] worked on Job Satisfaction in Public Sector and Private Sector: A Comparison. Their main findings are given below : Public Sector versus Private Sector comparisons are a debate which seems to be a never ending topic. It is very difficult to take stand for either of these two forms of administration. The reason behind that is not unknown but obvious as both provide scopes in different ways. Job satisfaction describes how content an individual is with his or her job. The happier people are within their job, the more satisfied they are said to be. This paper surveys both the sectors in most of the aspects of analysis.. As the current findings show, jobholders vary regarding the extent of ambivalence experienced with respect to their attitude toward their job. The current findings also open up opportunities for further research regarding the consequences of job ambivalence. For instance, the present findings imply that job performance of individuals with high versus low job ambivalence may fluctuate such that job performance is comparatively high when positive beliefs and affective experiences are salient and thus predominate at a certain point in time but that their performance may be comparatively low at other times when negative beliefs and affective experiences are salient and predominate. In this respect, research could, for instance, collect manager perceptions of performance consistency. Future research should aim to replicate the present findings with larger and more diverse samples as well as profit from the use of multiple-item scales to measure job performance. Geeta Kumari and K.M. Pandey [11]studied on stress management problem of Avtar steel industries, Chennai, India. Their main findings are the followings. A sample size of 100 is taken for the purpose of analysis made from primary and secondary data. Out of the total sample most of the respondents are male and many are between 50 and above. Most of the respondents are under graduate and have professional qualification.
Most of the respondents have 10-15 years of long association with the organization. Almost all the respondents are satisfied with the physical and psychological working condition of the organization, and only fewer respondents are dissatisfied with the psychological working condition of the organization.
The opinion about the training programs conducted by the organization is almost better, according to majority of the respondents.
5. III.
6. Materials and Methods
712 Engineers and 114 Managers have been surveyed on their opinion regarding different qualitative aspects which can lead to efficient and happy working environment. Majority of employees surveyed indicated the importance of qualitative aspects (mainly not related to work). In EIL, lesser people switch jobs and the reason can be above qualitative aspects asked in survey fulfilled by EIL. Training is must to cope with the continual modernisation of both material resource and human resource like work culture / ethics, equipment etc. so that an organisation does not lag behind to others and always adds to the Skilled man power and hence productivity of an organisation. EIL, an organisation completely dependent on its manpower as it seek work in engineering consultancy, encourages training and even has a separate department in the organisation which arranges training for personnel.
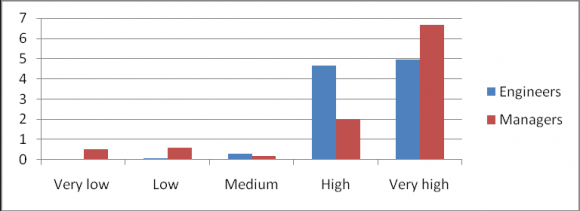
7. Do you think the place of sports in an organisation and special leaves granted to represent organisation in bigger forum helps?
It is observed from the bar chart 3 that in the survey conducted; there is a huge difference in the opinion of Engineers and Managers regarding sports. Managers generally old consider it rarely helpful for the employees while Engineers (younger) supported it asmany stated that it helps alleviate work pressure by providing a short break.
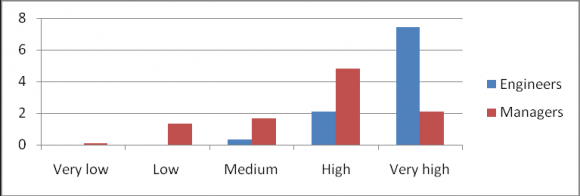
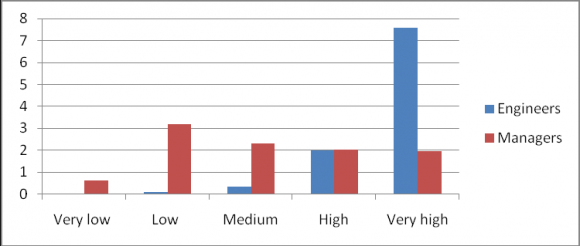
EIL do allow their employees to participate in tournaments generally held among public sector undertakings all over India and also hosts many tournaments in different sports occasionally. It is observed from the bar chart 8 that Employees were asked whether self service in nontechnical activities (like printing, Xerox, tea/coffee) shall be made mandatory, Engineers were more in the view that self service shall be encouraged to avoid growth of the feeling of grandeur or say disparity among employees which helps in the healthy working environment and avoid feeling of animosity. Managers do not seem to agree and provided the justification that it reduces the valuable time which can be spent in more work related activities and hence beneficial for the organisation to consume efficient hours of each employee in work related activities only. It is observed from the bar chart 11 that when asked about individual responsibility or decentralisation of execution of job responsibility, Engineers agreed that it reduces execution time and boosts "sense of confidence" and equips them to execute job more swiftly. However, Managers do not agree with this and emphasize on the significant chance of making an error in job execution which can ultimately result in delay of project. Managers seem to follow the proverb "prevention is better than cure" but engineers do not seem to believe in the conservative method and many a times entrepreneur, in general, young have given the conservative approach a fall back and made it obsolete using their own approach "No risk No gain". 12. Do you think working in a PSU adds up some 'psychological' feeling of job security in employees' mind? BAR CHART -12 It is observed from the bar chart 12 that Employees were even asked whether working in a PSU make them feel more secure as far as their job is concerned. Different opinion and result were spotted when engineers and managers were surveyed. Engineers were more of opinion that feeling of security shall be dealt with feeling of career stagnation as PSU generally follow conservative, passive and less risky approach to achieve their targets and hence generally lags behind private firms which follows aggressive and innovative approach to achieve higher growth which puts them in leap forward than PSUs. Managers were concerned with the volatility of market and extent of which it affects PSUs (lesser) than the private firms. Complete openness to the market reduces resilience of the organisation and which can lead to insecurity among the employees of the firm.
8. Conclusion
Refer BAR CHART-13, level of job satisfaction calculated were 82.2 % and 84.4 % for Engineers and Managers respectively. Employees seems highly satisfied with their organisation and so able to work efficiently which can be seen in increasing growth rate (refer Table -2 ) irrespective of adversity it faced like recession and still cruising to it keeping recent turmoil like high inflation, euro crisis etc. at bay.
During recession, when other organisations were issuing pink slips, Engineers India Limited recruited most (refer Table-1) due its demand in the market. As work increased with stupendous growth in Engineers India Limited, it increased its' manpower and lesser people switched before and after the recession as EIL has been emerging which can be seen in its' increasing growth / turnover (net profit), refer Table-2. Employees generally stick to the company if its market value does not fluctuate much which boosts them with the 'sense of security'. Being a PSU also adds to the same, however many PSUs which occur losses in India during this period recruited lesser and declining turnover made them narrow their manpower. Many qualitative aspects have been asked in the survey and there is one thing that can be concluded from the survey that now a day employees do not give importance to mere fiscal requirement but also to working environment which include many work related and non-work related aspects those have been asked in the survey. With the generation of more and more money in the market and work pressure on individual has been tantamount due to which employees seek for comfort in work and many things which may help alleviate work pressure and so their personal / social tension. Except some differences in few question asked in survey, in general majority seems to have similar opinion and agrees to the importance of good working culture inclusive of aspects which treats them more than a machine.
Aesthetic culture of EIL following many HR related aspects and ability to cope with the standard of facilities provided respective to other firms all over India makes it one of the best working places.